What is carbon fiber?
Carbon fiber is a kind of artificial high strength PAN-based fiber, which is usually saturated with a certain resin such as epoxy, polyester, vinyl ester, to become CFRP matrix with outstanding properties. The raw material used to produce carbon fiber is called precursor. It’s drawn into long strands and then heated to an extremely high temperature 1000℃ to 3000℃ without allowing it to be in contacted with the oxygen. So it won’t burn at such high temperature. Instead, the high temperature causes the atoms in the fiber to vibrate violently until most of the non-carbon atoms are expelled.This process is called carbonization and leaves a fiber composed of long, tightly interlocked chains of carbon atoms with only a few non-carbon atoms remaining. Then the fiber needs to be coated with certain resin, which can protect fiber from damage during weaving and winding. Finally the fibers are twisted into yarns of various sizes, such as 1k, 3k, 6k, 12k, 24k, etc.
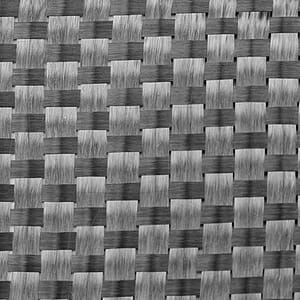
Carbon fiber can be weaved into different patterns, such as unidirectional, plain, twill, satin, etc. The unidirectional weave carbon fiber cloth is primarily applied in structural strengthening, seismic retrofitting, construction renovation, while it also could be used in boat construction and wind energy blade construction. The other 3 patterns are all bi-axial weave, which can give strength in both 0/90 directions. The bi-axial carbon cloth normally has stunning appearance which makes them popular in molding products for automotive, sports and even music. The final products made from carbon fiber are usually extraordinarily light and rigid. Thirty years ago, carbon fiber was a space-age material, too costly to be used in anything except aerospace. As the carbon fiber industry develops so fast in the past years, the price of carbon fiber has become much more acceptable, which makes it so popular these years.