The process of manufacturing fiberglass is called pultrusion. The manufacturing process for glass fibers suitable for reinforcement uses large furnaces to gradually melt the silica sand, limestone, kaolin clay, fluorspar, colemanite, dolomite and other minerals until a liquid forms. It is then extruded through bushings, which are bundles of very small orifices (typically 5–25 micrometres in diameter for E-Glass, 9 micrometres for S-Glass).
These filaments are then sized (coated) with a chemical solution. The individual filaments are now bundled in large numbers to provide a roving. These rovings are then either used directly in a composite application such as pultrusion, filament winding (pipe), gun roving (where an automated gun chops the glass into short lengths and drops it into a jet of resin, projected onto the surface of a mold), or in an intermediary step, to manufacture fabrics such as chopped strand mat (CSM), woven fabrics, knit fabrics or uni-directional fabrics.
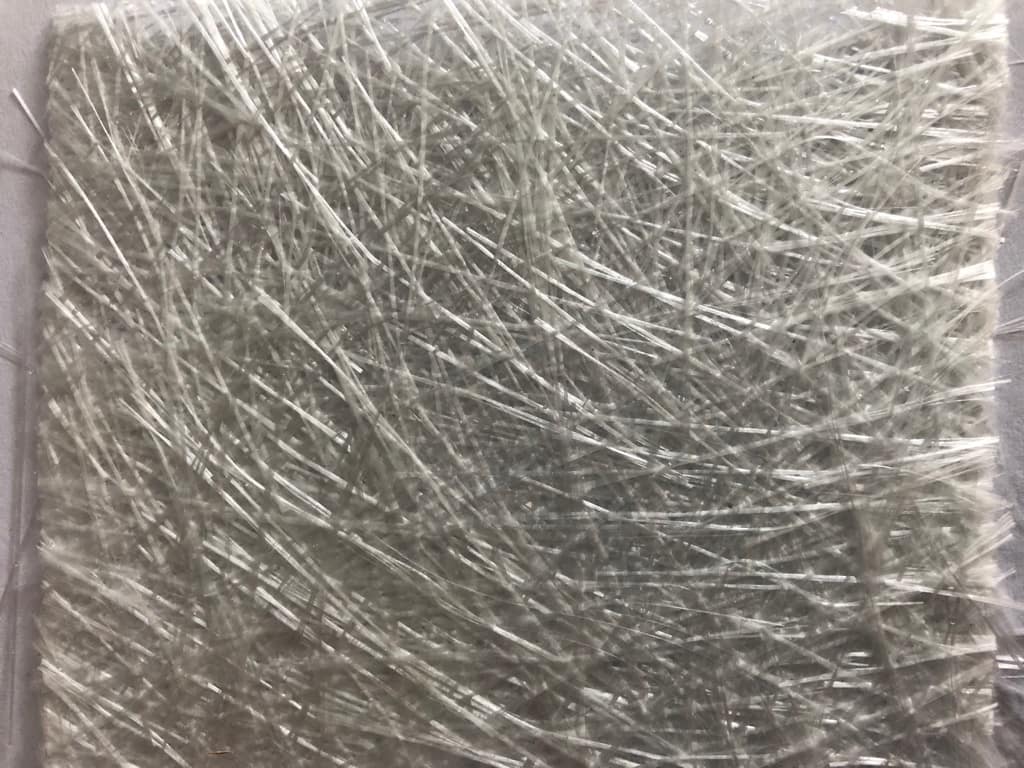
Fiberglass Chopped Strand Emulsion Mat (CSM) is made from E-glass low size chopped strands held together by an emulsion binder which makes it perfectly suitable for use with polyester, vinyl ester and urethane-acrylate resins. The basic strand has a sizing system containing a silane coupling agent.Polyester is the preferred resin for wetting out this form of glass fiber material as it readily dissolves the styrene bonding agent.
Applications
It’s often used in mold construction and parts where thickness is needed.
| Item | EMC300/EMC450/EMC600 |
| Type | E-glass fiber |
| Binder | Powder/Emulsion |
| Strength in 0˚direction | >30N/150mm |
| Strength in 90˚ direction | >30N/150mm |
| Combustible Content | 1.8-8.5% |
| Moisture | <0.2% |
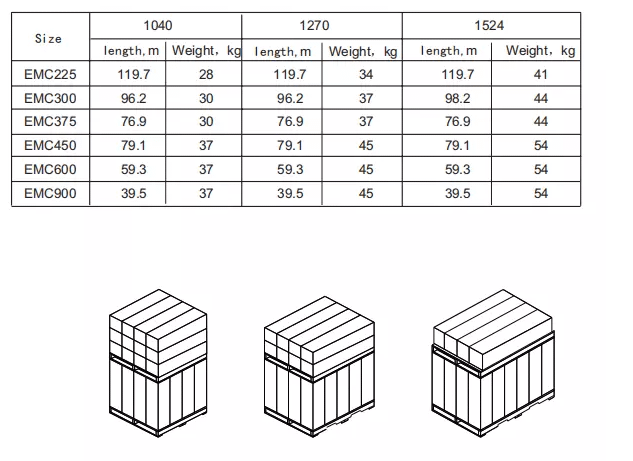
Packing
Any question or need more information?









